Breed Standard
Information shared from
Encl. 3b, Stockholm 4/6-12
00.00.0000 /EN/
FCI-Standard Nr: 000
PRAGUE RATTER
(Pražský krysařík)
Encl. 3b, Stockholm 4/6-12
brown and tan adult female
fawn male long haired adult male
brown and tan female
black and tan female
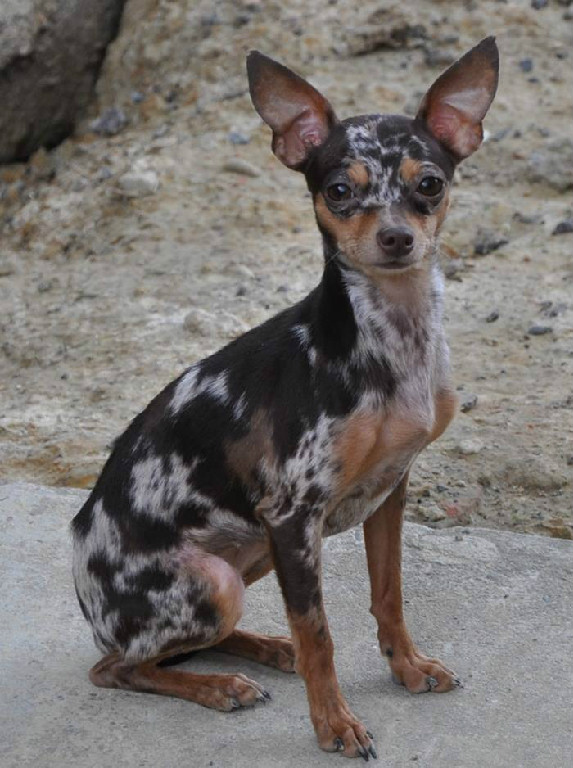
brown merle
blue merle
short haired puppy
long haired puppy
ORIGIN: Czech Republic.
UTILIZATION: Companion dog.
FCI-CLASSIFICATION:
Group 9 – Companions and Toy Dogs.
Section 9 Continental Toy Spaniels
Russian Toy and Prague Ratter.
Without working trial.
BRIEF HISTORICAL SUMMARY:
Historically, this breed has been known since the remote past of the Czech state. Because of its small size, quick movement and highly developed sense of smell it was used for killing rats (which gave it the name "Krysarík" = Ratter). This quality was gained during its long historical development. This small active dog was often seen at aristocratic feasts of Czech kings at the Prague castle. It adorned courts of Bohemian aristocracy and as a gift from Bohemian kings it came to other European rulers and later to the ordinary citizens. The search of historical facts resulted in proofs that this breed really is of Bohemian origin and can be traced to the early history of the Czech nation. In 1980 its regeneration successfully started. Pražský Krysarík is again a favorite pet that lives as a family dog and is becoming popular also in other countries of in the world.
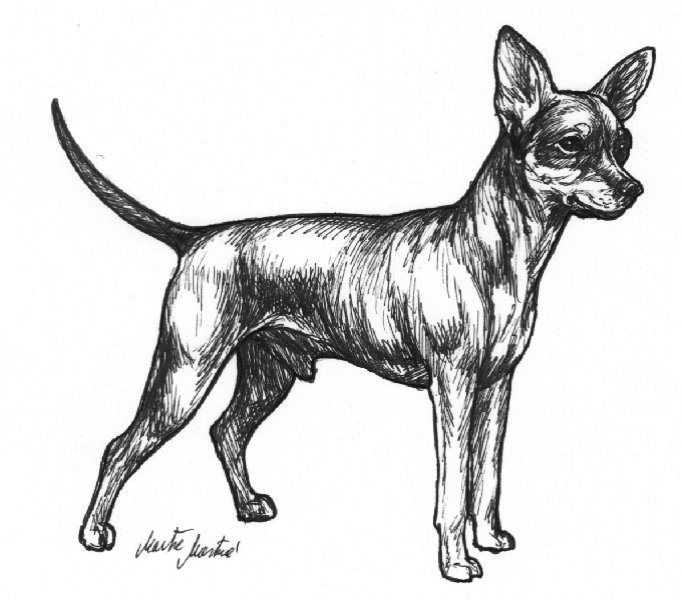
GENERAL APPEARANCE:
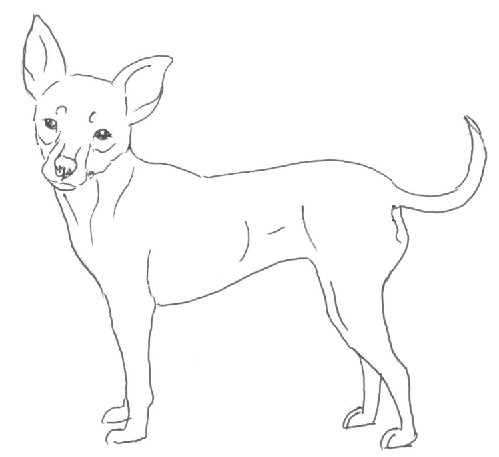
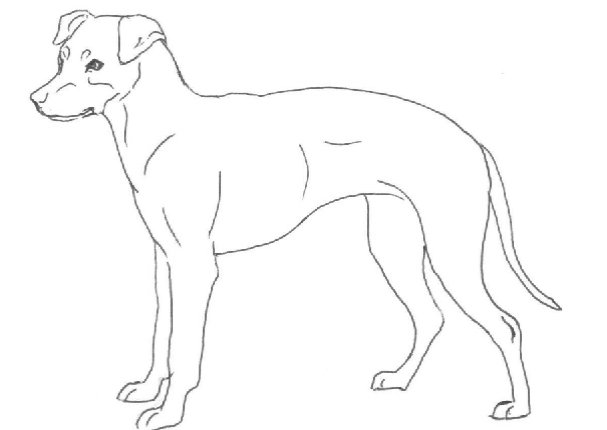
A small smooth-haired or medium long coated dog with an almost square and compact body. Despite its small size it is a very active, alert and lively dog. Sexual dimorphism should be clearly defined.
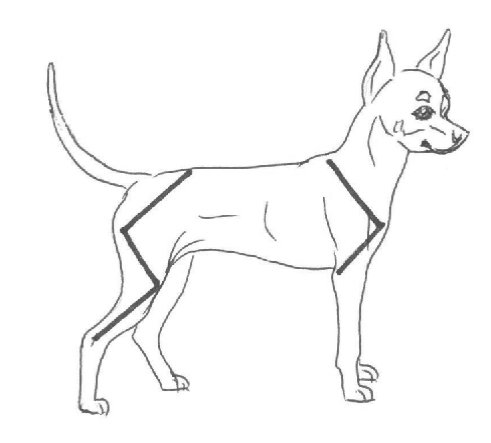
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS:
Height at withers to length of body: 1 : 1.05 – females might be longer.
Depth of chest 45 -50% of the height withers.
Skull width to skull length 1 : 1 to 1.03.
Length of foreface 1/3 -1 of the head length.
These measurements and proportions should be regarded as ideal, but the general appearance is more important.
BEHAVIOR/TEMPERAMENT:
Gentle, curious and tender. Quick with good movement and steady pace. By nature slightly reserved towards strangers but very friendly in the family. With natural nobility and character.
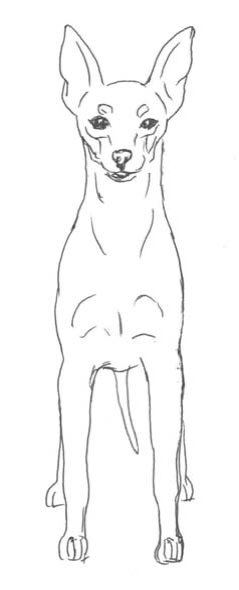
HEAD
CRANIAL REGION:
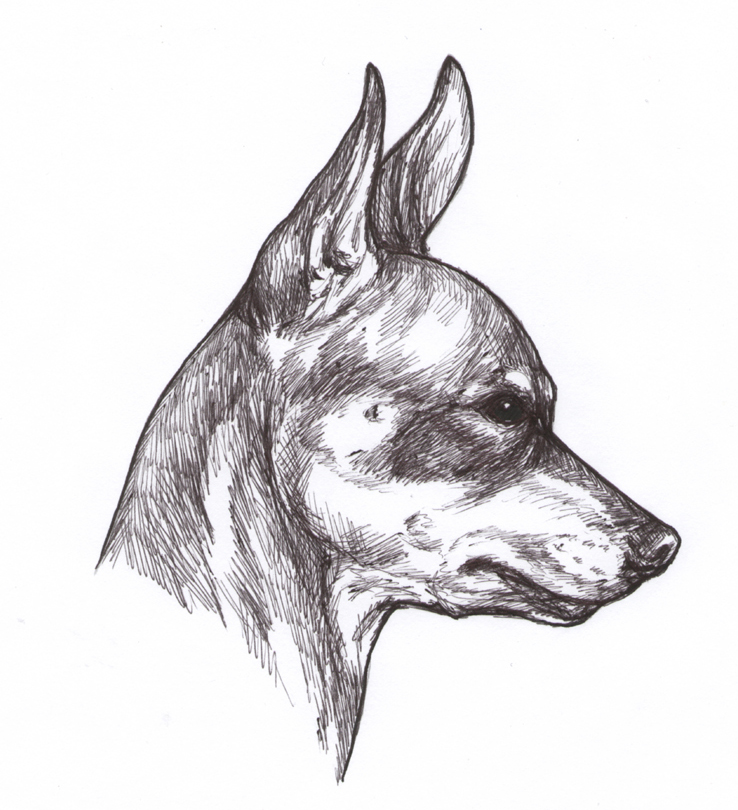
Skull: Rounded, not parallel with nose, occiput is visible. Eyes are set wide apart.
Skin on skull has no folds and is coated with short and fine hair, except in the case of long coated dogs. In this case the skin can be coated with longer hair.
Stop: Distinct.
FACIAL REGION:
Nose:
Fully pigmented and color according to coat color.
Lips:
Close-fitting, firm and closed lip corners. Lip edges fully pigmented and color according to coat color.
Jaws/Teeth:
Firm and converge to muzzle. Regular scissor bite. Preferably with no teeth missing.
Eyes:
Dark, color according to color of the coat. Medium sized, rounded, no exaggerated bulging, set wide apart. Lids tight-fitting and well pigmented.
Ears:
Set at the back of the head, triangular, firm, naturally erected, carried in a gentle angle to the sides.
NECK:
Neck without folds, gracefully curved and sufficiently long, at the right angle to body and head.
BODY:
Top line:
Level and firm.
Withers:
Not visible.
Back:
Short, straight, firm.
Loin:
Short, coupled.
Croup:
Gently inclined.
Chest:
Oval in cross-section. Chest depth forms 45 – 50% of the height at the withers.
Underline and belly:
Abdomen is slightly drawn-in, between abdomen and loins clearly merging into drawn-in flank.
TAIL:
Set just below the level of the top line, docked in country of origin. If not docked, it can reach no further than to the hock. The tail is firm and gets narrower to the tip. The tail is straight half way up and carried slightly upright. When the dog is moving it is carried higher, it can be curled over the back in a semicircle.
LIMBS
FOREQUARTERS:
General appearance:
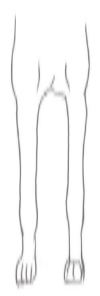
Viewed from the front straight, parallel and legs should not stand very broad.
Shoulder and upper arm:
Muscular, close to the chest. Angle not too obtuse.
Elbow:
Set close, straight. Turned neither out nor in.
Forearm:
Adequately strong, straight.
Metacarpus (Pastern):
Viewed from the front, a fluent continuing of forearm. Viewed from the side, has a slight angle, solid.
Forefeet:
Round, firm, with well arched, tight toes. Nails dark.
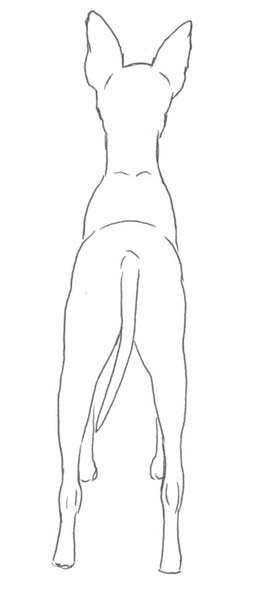
HINDQUARTERS:
General appearance:
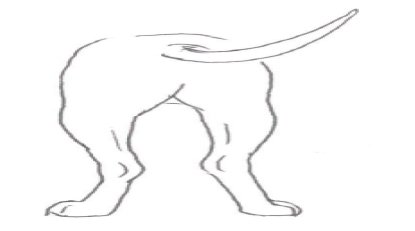
Muscles well developed, viewed from the side, stifle joint to be well bent and hocks well angulated. Viewed from behind, the dog should stand solidly, parallel and legs not too wide apart.
Hind feet:
Same as the forefeet but might be a little longer.
GAIT / MOVEMENT:
Both forequarters and hindquarters should produce steady, flowing, parallel, light movement. Pads must not drag along. Hind feet to step fully into traces of forequarters.
SKIN:
Skin is tough, strong, firm and fits tight to body. Pigment according to the color of the coat.
COAT:
1) Short coated -
Short, glossy, fitting close to body, thick, without bald places. Head is usually coated with thinner and shorter coat than the body.
2) Long coated -
Medium long, fringes on ears, quarters, tail and slightly more open on the chest.
Color:
Black and tan, brown and tan and other lighter nuances, also yellow recessive color, merle and red. Tan is red, deep and most desired is a dark red tan, well marked. Tan markings are found above eyes, on cheeks, on chest and on the pasterns of the forefeet. Also on the feet, inside the hindquarters and under the root of the tail. On the fore chest it forms two similar and separated triangles. Colors different from black and tan differ in the basic color of the coat, nose, and eye and markings. Deeper pigmentation is preferable.
SIZE AND WEIGHT:
Height at the withers:
Males and Females: ideal 20-28 cm
Weight:
Males and Females: Ideal 2,6 kgs.
FAULTS:
Any departure from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree and its effect upon the health and welfare of the dog.
- Narrow or insufficiently arched skull.
- Asymmetrical bite.
- Slightly arched back and loins, softer back.
- Feet slightly curving out-or inwards.
- Excessive tan markings on head, abdomen, not separated markings on the chest.
- Excessive tan markings on upper lip
- Big white spot on the chest (more than 1cms).
- No white spots on toes.
- Black hairs in the red tan color.
- Permanently curled tail, tail closely lying to one side, low-set tail.
- Long body with short legs.
- Nose not pigmented.
DISQUALIFYING FAULTS
- Aggressive or overly shy dogs.
- Any dog clearly showing physical or behavioral abnormalities shall be disqualified.
- Open fontanelle.
- Apple shaped head
- Too short in muzzle it means that foreface does not make 1/3 of the length of the head.
- Blue or predatory eye (very pale yellow).
- Overshot bite.
- Hanging ears
- Strongly arched back and loins.
- Bald spots on any part of the body.
- More than 4 teeth missing (except P1 and M3), 2 or more incisors missing.
- Tan marked dogs that lack tan markings on the head.
- Large white mark on the chest, more than 2cms and white markings anywhere on body or legs.
- Excessive black overlay obscuring the tan markings.
- Size over 28 cms or under 20 cms.
N.B: Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into the scrotum.
ILLUSTRATONS of the Prague Ratter/Pražský Krysařík
Typical Male
Typical Female
Head
Coat Types
Short coat variety
Long coat variety 1
Long coat variety 2
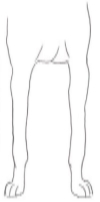
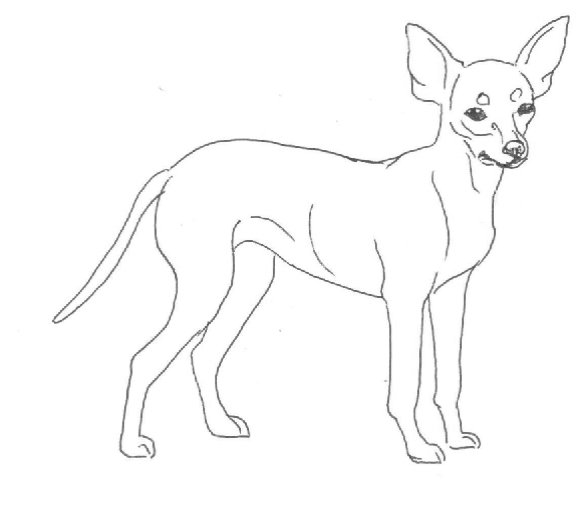
Body Position – General Conformation
Correct
Incorrect
Angularity
Good
Too Severe
Not Enough
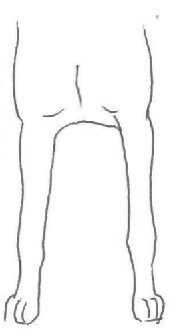
Structure
Correct
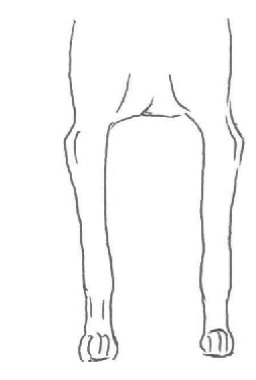
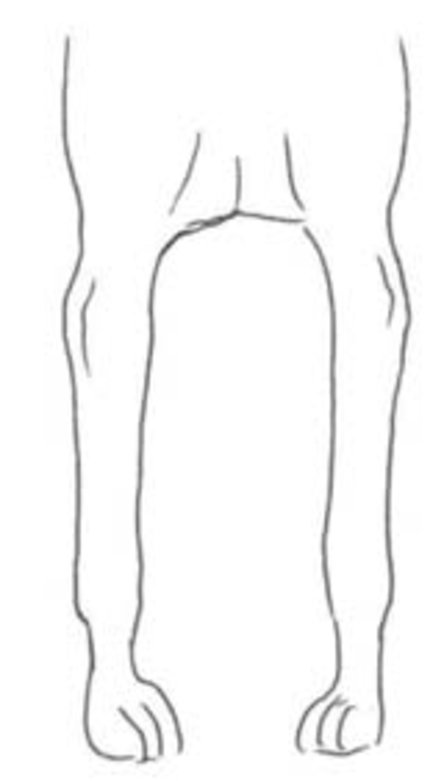
Front view
Poor conformation examples
Rear View
Poor conformation example
Back/Top line
Poor conformation example